In one of the largest cybercrime crackdowns in history, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) recently announced the seizure of approximately $15 billion worth of Bitcoin connected to a sprawling international fraud scheme. The operation, allegedly masterminded by Chen “Vincent” Zhi, CEO of Cambodia’s Prince Holding Group, marks the largest cryptocurrency forfeiture ever executed by the department.But this case isn’t just about financial figures or legal victories it’s a disturbing look into a scam that blends human trafficking, emotional manipulation, and digital deception. Known as the “Pig Butchering” scam, it’s one of the most insidious forms of online fraud today, preying on loneliness and trust while draining victims’ savings across the globe.
What Is the “Pig Butchering” Scam?
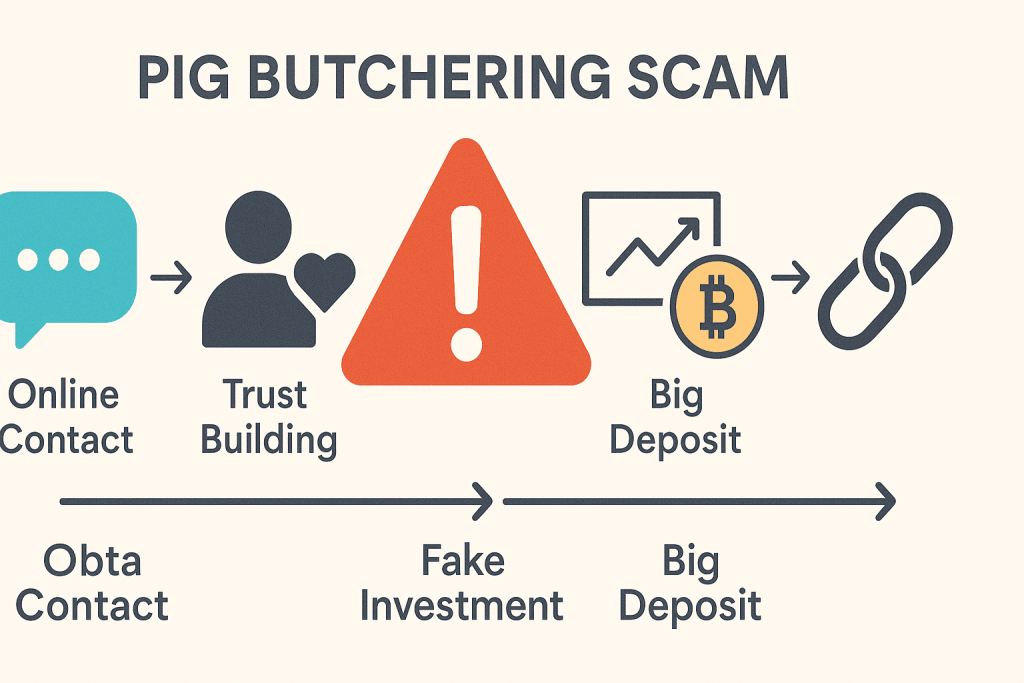
The term “pig butchering” comes from the analogy scammers use to describe their victims. Like fattening a pig before slaughter, fraudsters first build emotional rapport, often over weeks or months, before “butchering” that is, convincing victims to invest large sums into fraudulent cryptocurrency or investment platforms.
It usually starts with an innocent message, perhaps a wrong number text, a social media connection request, or a match on a dating app. The scammer appears charming, patient, and intelligent, slowly establishing a bond. Once trust is secured, they introduce what seems like a lucrative investment opportunity, often backed by fake websites, charts, and testimonials.
Victims, feeling connected and convinced, invest and may even see fake “profits” at first. But when they try to withdraw funds, the money vanishes, and so does the scammer.
The Prince Holding Group Connection
Authorities allege that Prince Holding Group, a multinational conglomerate with major real estate and investment holdings across Cambodia and Southeast Asia, was secretly operating cyberfraud compounds behind its corporate facade.
According to U.S. federal prosecutors, CEO Chen “Vincent” Zhi and associates forced trafficked workers many lured under false promises of legitimate employment to carry out romance and investment scams targeting Westerners.
These victims of trafficking were forced to manage fake profiles, initiate online relationships, and manipulate unsuspecting individuals into transferring cryptocurrency to sham investment accounts controlled by the network.
The U.S. Department of Justice and U.K. authorities have since imposed economic sanctions on Prince Holding Group and its affiliated entities, labeling them a “transnational criminal organization.”Zhi, who remains at large, now faces wire fraud and money laundering charges filed in a New York federal court.
The Scale of the Scam
The numbers are staggering. According to the U.S. Treasury Department, Americans lost over $10 billion to scams originating from Southeast Asia in 2024 alone a 210% increase in deposits and a 40% rise in overall scam revenue compared to 2023.
These scams aren’t limited to the United States. Victims span across Europe, the UK, Canada, and Australia, highlighting how deeply global and coordinated these fraud operations have become.In most cases, the victims never see their funds again, as scammers quickly convert stolen crypto into privacy coins or launder it through complex blockchain transactions that make recovery almost impossible.
How “Pig Butchering” Scams Operate Step-by-Step
Understanding the anatomy of this scam can help potential victims spot red flags early.
1. The Hook
Scammers make contact through casual channels: a “wrong number” text, an Instagram message, or a dating app. They start out friendly, curious, and non-intrusive.
2. The Bond
Over weeks, they build emotional trust sharing daily updates, expressing affection, and pretending to invest time in the relationship. Victims feel emotionally validated.
3. The Lure
Once trust is solid, the scammer introduces the idea of “smart investing.” They’ll show screenshots of supposed profits or share access to a fake trading app that looks legitimate.
4. The Investment
The victim deposits a small amount, sees a quick “profit,” and is encouraged to invest more. The scammers simulate returns using manipulated dashboards.
5. The Butchering
When the victim invests a large sum or tries to withdraw, the system suddenly “freezes,” or the scammer disappears. The emotional and financial loss is devastating.
Why These Scams Are So Effective
1. Emotional Manipulation
Scammers use psychology and empathy as weapons. They often mirror their victim’s interests or pretend to share personal struggles, creating a sense of intimacy.
2. Sophisticated Technology
Fake trading websites often look identical to real investment platforms, complete with charts, dashboards, and customer support.
3. Social Engineering
Scammers understand human emotions, loneliness, greed, trust, and hope and use them to cloud victims’ judgment.
4. Lack of Awareness
Because many victims are embarrassed to report being duped, law enforcement often underestimates how widespread these operations are.
The Human Trafficking Element
Perhaps the most disturbing part of this criminal web is the use of trafficked labor.
Reports reveal that many of the individuals behind scam messages are not willing participants they are victims themselves.
Young workers from countries like Myanmar, Vietnam, and the Philippines are lured to Cambodia or Laos with promises of high-paying tech jobs. Once there, they’re stripped of passports and forced into scam compounds, working up to 16 hours a day under threat of violence.
This brutal system has turned cybercrime into a modern form of slavery, where victims on both sides of the screen suffer exploitation.

How to Protect Yourself from Pig Butchering Scams
- Be Skeptical of Sudden Online Friendships
If someone you barely know starts discussing investments, that’s a red flag. - Never Invest Based on Personal Relationships Alone
Genuine investors and traders will never ask for personal transfers or insist on using private apps. - Verify Platforms
Before transferring crypto or funds, research the company. Use only regulated exchanges and verify domain authenticity. - Don’t Fall for “Guaranteed” Profits
No legitimate investment guarantees instant or risk-free returns. - Report Suspicious Activity
Victims should contact the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) or local authorities. The faster you report, the higher the chance of tracing stolen assets.
A Global Wake-Up Call
The DOJ’s $15B Bitcoin seizure is more than just a legal milestone it’s a global wake-up call. It exposes the interconnected world of romance scams, human trafficking, and crypto fraud, reminding us that digital crimes are not isolated but part of a larger, organized network.
As technology continues to evolve, scammers are finding new ways to exploit human emotions and digital loopholes. Awareness and education remain the strongest tools we have to fight back.
Trusted & True remains committed to providing reliable, research-based insights into online safety, fraud prevention, and cybersecurity awareness helping you stay informed and protected in the digital age.











